Recognizing that our business activities are supported by a sound global environment, we are working to reduce environmental risks that affect biodiversity and contribute to the maintenance and conservation of biodiversity, with the aim of realizing a sustainable and prosperous society. We have endorsed the “Keidanren Initiative for Biodiversity Conservation” by KEIDANREN (Japan Business Federation) and make donations to the Keidanren Nature Conservation Fund.
For information about the “Keidanren Initiative for Biodiversity Conservation” and the list of companies and organizations that have endorsed this initiative, please click here.
An abundant global environment (ecosystem) not only brings food, water, and other blessings to our lives, but it also contributes to mitigating climate change and disasters, restricting the generation of infectious agents, parasitic insects, etc., and stabilizing mental and cultural conditions, as well as plays an extremely important role for our health. So that we can pass on a rich global environment to the next generation, we assess the dependencies and impacts of our business activities on the global environment and promote a range of activities (environmental impact assessment of pharmaceutical products, management of chemical substances, management of genetically modified organisms and pathogens, pollution control of air, water, and soil, etc.) to minimize these impacts. While contributing to people’s health through the creation of innovative new medicines, we will also work together with local governments, NPOs, NGOs, and other stakeholders to help achieve “nature positive” by 2030 – halting and reversing the loss of biodiversity to put nature on track to recovery - through our ongoing initiatives.
In FY2024, we have identified the nature-related risks and opportunities within our business activities in line with the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) final recommendations (v1.0). We will appropriately disclose information not only on climate change but also on biodiversity. For more details, please see the page of our website titled “Information disclosure based on the TNFD recommendations.”

The API (including its metabolites if it was administrated to human) produced by the manufacturing process, or discharged into the environment through excretion after the proper use and disposal of medicines may affect ecosystems due to their physiological effects, as well as their physicochemical and biological properties. In our manufacturing plants, we consider the scientific characteristics of API, implement deactivation treatments, such as oxidative decomposition, reduction, and alkaline hydrolysis and prevent the release of API into the environment. We also estimate occupational exposure limit (OEL) based the results of animal testing and human clinical trials and define an API in Category 4 (chemical substances with OEL lower than 10 μg/m3) or higher as "highly active API." All wastewater containing highly active API is outsourced to be incinerated and we do not discharge it into the environment.
We appropriately conduct the environmental assessment of API in accordance with local guidelines. We predict the hazards to the environment of new drug application candidates and launched APIs based on the in silico quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR), and we list the results on safety data sheets (SDS). We also evaluate the effects on aquatic organisms sequentially for launched APIs and disclose the results on SDS.
We are working to reduce the use of chemical substances. We are also committed to reducing emissions of chemical substances not only in compliance with laws and regulations but also in recognition that these emissions may impact human health and the ecosystem.
In accordance with the law concerning “Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR),” we have appropriately controlled chemical substances that may have harmful effects on human health and ecosystems. In FY2024, the amount of PRTR Class 1-designated chemical substances handled in an amount of 1 ton or more was 1.7 tons, and their associated emissions into the air was 0.0 tons (the vaporized solvent was adsorbed and removed by activated charcoal installed in the smoke control system). Even with the addition of acetonitrile, which has been excluded from the PRTR Class 1-designated chemical substances since FY2023, the handling amount and emissions into the air were 7.8 tons and 0.3 tons, respectively. Emissions into the environment remain at a low level. We also legally and appropriately manage chemical substances other than those reported. We will continue to work to reduce emissions into the environment through appropriate chemical substance management.
Waste containing PCB is disposed of appropriately in compliance with the "Act on Special Measures concerning Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes." As of the end of March 2025, there is no high-level or low-level PCB-containing waste in our storage. We only have two electrical transformers containing low-level PCB (in use). We plan to entrust them to a treatment company that has permission to dispose of low-concentration PCB waste within the treatment deadline of March 31, 2027, which was stipulated in the above law, and dispose of them properly.
| PCB waste | Type | Classification | Number of units |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-concentration PCBs waste (PCB concentration: Greater than 0.5%) |
Capacitor, etc. | In use | 0 |
| Storage | 0 | ||
| Low-concentration PCBs waste (PCB concentration: 0.5% or less) |
Transformers, etc. | In use | 2 |
| Storage | 0 |
The management of radioisotopes is conducted appropriately in accordance with the "Act on Prevention of Radiation Hazards due to Radioisotopes, etc." and the results are reported to the Nuclear Regulation Authority as a radiation management status report every fiscal year.
As for genetically modified organisms and pathogens used in drug discovery research and manufacturing activities, we are preventing their spread into the environment and their leakage by complying with in-house regulations based on relevant laws and regulations such as the “Act on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biological Diversity through Regulations on the Use of Living Modified Organisms” (Cartagena Act) and the “Act on the Prevention of Infectious Diseases and Medical Care for Patients with Infectious Diseases” (Infectious Diseases Control law). In addition, to promote the appropriate use of these research samples, the in-house committee on biosafety continues to provide education and training to laboratory staff and conduct examinations on the experimental applications.
In the manufacturing plants and research institutes, we comply with the "Air Pollution Control Act", the "Water Pollution Control Act", the "Sewerage Act", the "Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act", the "Act on the Assessment of Releases of Specified Chemical Substances in the Environment and the Promotion of Management Improvement", and conclude agreements on pollution prevention with local governments, in order to reduce our environmental impact.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and smoke dust (particulate matter: PM) are measured as air pollution indices. NOx emissions in FY2024 remained low at 6.0 tons. Since none of our facilities use high-sulfur content fuels (heavy oil, coal, etc.), we are maintaining SOx emissions at a very low level of 0.0 tons. PM emissions in FY2024 were also maintained at a low level of at 0.3 tons.
To prevent water pollution, wastewater from manufacturing plants and research institutes is controlled under the stricter standards agreed with local governments or under our voluntary and stricter standards in addition to standards related to relevant laws and regulations. A public sewage system has not been developed at the Fujiyama Plant. Therefore, wastewater generated from business activities at the Fujiyama Plant is treated with sedimentation, activated sludge, pH adjustment, and disinfection at our on-site wastewater treatment facility. After cleaning wastewater, the water quality is checked, and then discharged to a river. Wastewater generated from business activities at the Yamaguchi Plant is treated with primary processes such as disinfection at on-site facility, followed by secondary processes at a treatment facility in the industrial park, and then discharged to a river. The biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), an index of wastewater quality, of wastewater discharged to public rivers in FY2024 was remained low at 0.14 tons. In addition, we conducted Whole Effluent Toxicity (WET) tests, which are toxicity tests using the biological responses of daphnia, algae and fish, on wastewater discharged into rivers or public sewage systems from the Fujiyama Plant, the Yamaguchi Plant and the Tsukuba Research Institute, and confirmed that there were no toxic effects on aquatic organisms. We plan to conduct the WET tests at all manufacturing plants and research institutes by FY2025. In preparation for an emergency event in which wastewater containing hazardous substances could flow into the drainage system, we have installed a storage tank to store wastewater, and for the wastewater containing highly active API, we have separated the possible flow from the drainage system by setting up a dedicated collection tank.
| Drainage site | Scope | Unit | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | Total | Production and research sites | Ton | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.79 | 0.77 |
| Sewerage system | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.66 | 0.64 | |||
| River | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
We provide thorough control of hazardous substances to prevent soil pollution. Measures are taken to prevent reagent bottles containing dangerous or hazardous materials from falling over on storage shelves. We also implement regular leakage checks on drainpipes and are replacing them with quake-resistant flexible pipes. If soil pollution is found, we will consult with the government and take appropriate measures, such as for the prevention of spreading and for purification measures, etc.
In recent years, extreme weather events are occurring as a result of global warming. We have formulated manuals to prepare for accidents and emergency situations caused by such weather, and we organize training sessions to minimize environmental impacts. In addition, we conduct drills every year in preparation for accidents and emergencies that may lead to water pollution and soil contamination.
The impact of our business on the environment was converted into monetary values using the Life-cycle Impact assessment Method based on Endpoint modeling (LIME) 3, a type of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). We divided our business activities into four damage assessment categories and assessed them. Namely, these categories were human health, social assets (impact from the consumption of fossil fuels and mineral resources), biodiversity, and primary production (impact from wastes and the use of land and forests). The environmental impact from the consumption of social assets was the highest (358 million yen), followed by human health (76 million yen), biodiversity (59 million yen), and primary production (0.6 million yen). The main factors affecting the environment in our business were energy consumption, such as electricity and city gas in terms of inputs such as resources and raw materials required for our business activities, as well as greenhouse gas emissions in terms of outputs generated by our business activities. We will strive to reduce our environmental impact based on these results.
On this occasion, we quantified the environmental impact of each business site, such as factories and laboratories, using a simplified LCA. In the future, we will conduct a simplified LCA for each of our products to evaluate their environmental impact.
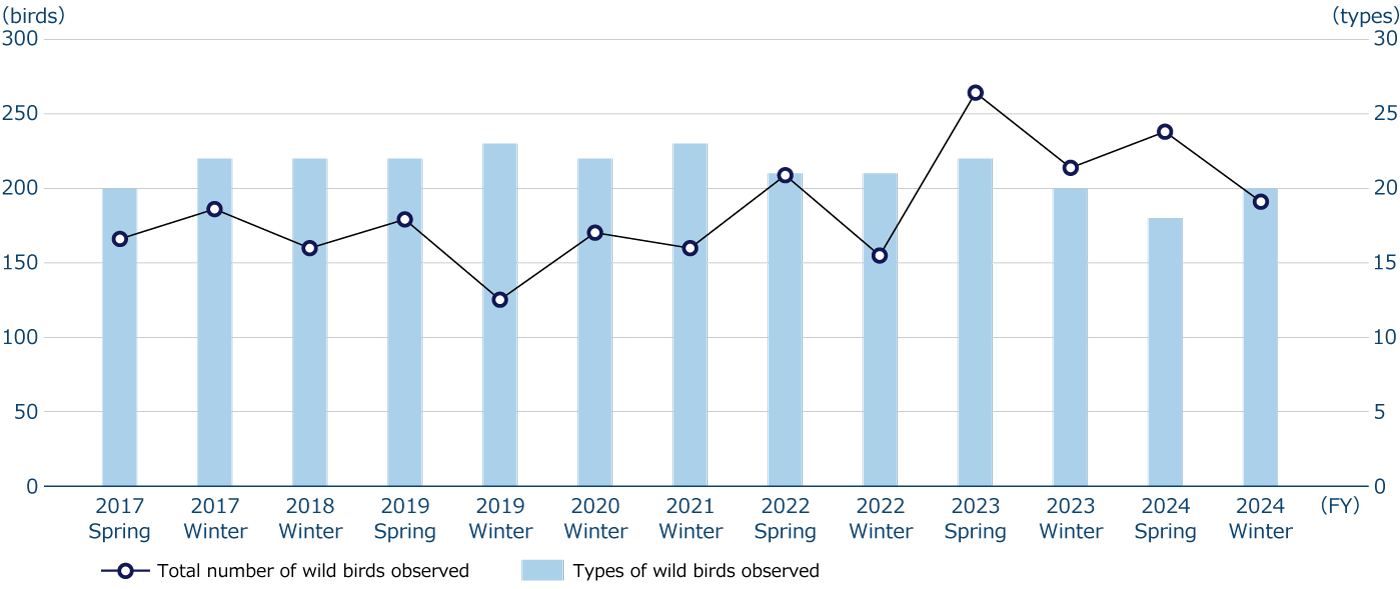
The Fujiyama Plant, one of our main plants, has a green space (36,000 m2) on its premises that is almost equivalent to the size of a baseball stadium. Since 2017, we have adopted conservation activities (community contribution activities) through wild bird surveys as an environmental goal based on our environmental management system (ISO14001). Every year, during the spring breeding and wintering seasons, we request the Wild Bird Society of Japan to conduct surveys* (up to four times a year) and use the results of those surveys as the basis for efforts to protect the abundance of biodiversity in the Fujiyama Plant (establishing green zones that are intentionally not mowed, planting trees that birds like, maintaining ponds and waterways, etc.). There has been no significant change in the species and total number of birds observed over an eight-year period, which can be interpreted to mean that ONO's production activities have not had a significant impact on nature. These results are also shared with Fujinomiya City and utilized in conservation activities related to biodiversity in local communities.
Wild birds surveys in the Fujiyama Plant
 Waterways within the factory (watering holes for wild birds)
Waterways within the factory (watering holes for wild birds)
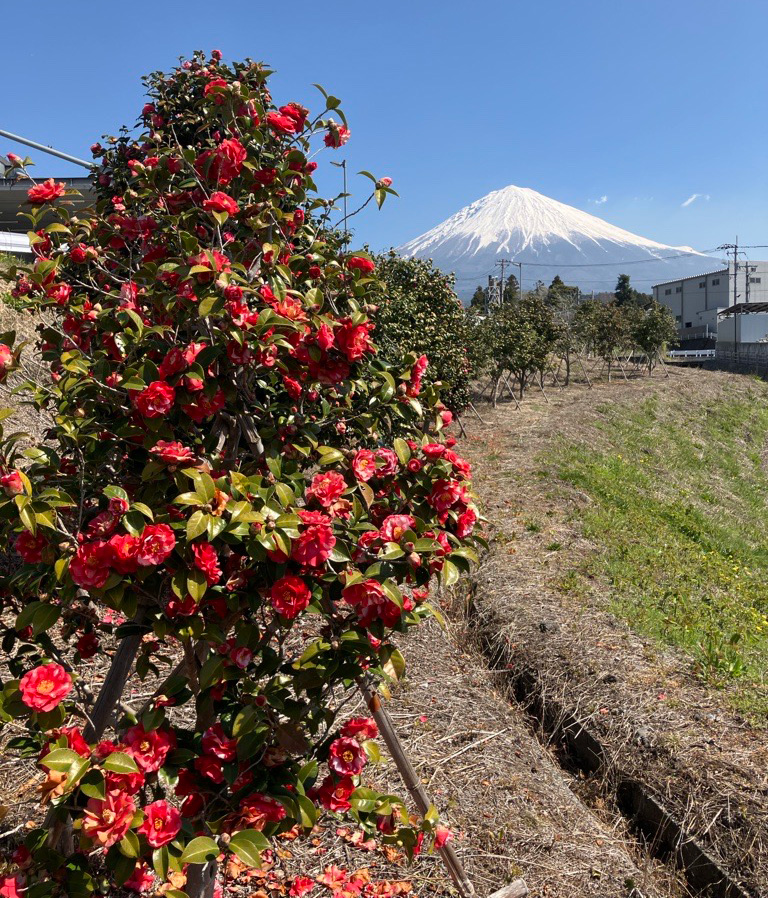 Planting camellia trees favored by Japanese white-eyes and brown-eared bulbuls
Planting camellia trees favored by Japanese white-eyes and brown-eared bulbuls
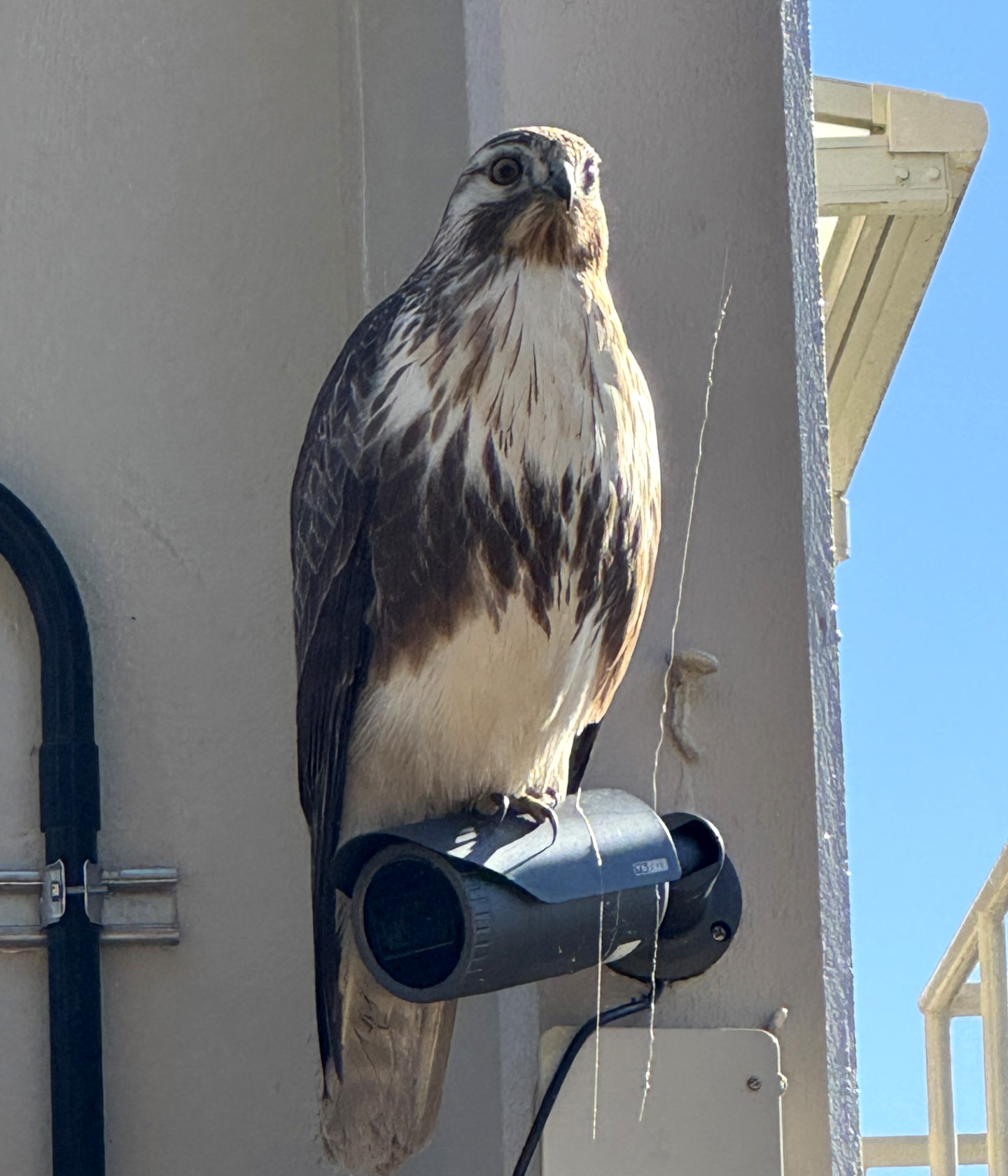 A common buzzard (Accipitriformes, Accipitridae) observed in December 2024
A common buzzard (Accipitriformes, Accipitridae) observed in December 2024
 A meadow and thicket within the factory
A meadow and thicket within the factory
 Pheasants that live in the meadow (Galliformes, Phasianidae) observed in May 2024
Pheasants that live in the meadow (Galliformes, Phasianidae) observed in May 2024