Even today as we see remarkable developments in the medical field, there are many diseases against which no effective treatment exists. Also, in low- and lower middle-income countries, there are many people who have difficulty receiving necessary medical care due to various reasons such as inadequate medical infrastructure and poverty.
Under the corporate philosophy “Dedicated to the Fight against Disease and Pain,” we aim to improve access to healthcare by pursuing these goals: Research and development of innovative new drugs and strengthening healthcare infrastructure.
In "Research and Development of Innovative New Drugs," we are actively engaged in the research and development of drugs for NCDs (noncommunicable diseases), including cancer, where medical needs have yet to be met, as well as for rare diseases. In addition, we are also strengthening our efforts so that we can provide new drugs to patients around the world, including Europe, the United States and Asia.
In the area of "strengthening healthcare infrastructure," we are working on medium- to long-term initiatives to train medical personnel and improve the medical environment in low- and middle-income countries through partnerships with NPOs, public institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and other organizations.
We set the improvement of access to healthcare as one of the themes included in the materiality "Enhancement of Social Trust" and the Board of Directors and the Management Meeting are managing targets and progress (Please click here for detail). In addition, in terms of implementation, the Sustainability Promotion Committee, consisting of members of each division, mainly promotes implementation under management by the Sustainability Strategy Meeting.
Based on our corporate philosophy of "Dedicated to the Fight against Disease and Pain," we have created a series of innovative new drugs that had been thought to be impossible in order to realize our passion to help people who are suffering from disease. We will take on the challenge of research and development of innovative drugs in collaboration with the world’s top scientists, contribute to people’s health by providing safe, secure and appropriate drugs, and take on the challenge of realizing a sustainable society through responsible business activities.
For more details about our business activities, please click here.
We believe that our efforts in the clinical development of pharmaceuticals for rare and pediatric diseases are critical to improving access to healthcare, and we are working as follows:
| Product name | Therapeutic indication* | Date designated as an orphan drug | Development Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPDIVO intravenous infusion | Malignant melanoma | June 17, 2013 | Approved |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | March 16, 2016 | Approved | |
| Malignant pleural mesothelioma | December 1, 2017 | Approved | |
| Cancer of unknown primary | March 11, 2021 | Approved | |
| Malignant mesothelioma (excluding malignant pleural mesothelioma) | February 22, 2023 | Approved | |
| Unresectable advanced or recurrent epithelial skin malignancies | May 23, 2023 | Approved | |
| Unresectable advanced or recurrent microsatellite instability-high (MSI-High) colorectal cancer | September 20, 2024 | Approved | |
| Demser Capsules | Improvement of catecholamine excess and various symptoms in pheochromocytoma | May 25, 2015 | Approved |
| Kyprolis for intravenous infusion | Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma | August 20, 2015 | Approved |
| Onoact for intravenous infusion | Life-threatening refractory and emergent cardiac arrhythmias: ventricular fibrillation and hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia | August 24, 2016 | Approved |
| Mektovi Tablets | NRAS or BRAFV600 mutation-positive malignant melanoma | December 4, 2013 | Approved |
| Braftovi Capsules | BRAFV600 mutation-positive malignant melanoma | December 4, 2013 | Approved |
| Unresectable, advanced or recurrent colorectal cancer with BRAF-mutation | June 19, 2024 | Approved | |
| Velexbru Tablets | Primary central nervous system lymphoma | August 20, 2019 | Approved |
| Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma | November 19, 2019 | Approved |
| Product name | Therapeutic indication | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Onon Dry Syrup | Bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis | Approved |
| Emend Capsules | Digestive symptoms (nausea, vomiting) resulting from the administration of antineoplastic agents (cisplatin, etc.) (including the delayed phase) | Approved |
| Proemend for intravenous injection | Digestive symptoms (nausea, vomiting) resulting from the administration of antineoplastic agents (cisplatin, etc.) (including the delayed phase) | Approved |
| Orencia for intravenous infusion | Active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis | Approved |
| Demser Capsules | Improvement of status of catecholamine excess secretion in patients with pheochromocytoma | Approved |
| OPDIVO intravenous infusion | Relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma | Approved |
| Rhabdoid tumor | Phase 2 | |
| Onoact for intravenous infusion | Tachyarrhythmia (supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in patients with low cardiac function | Approved |
We strive to continually develop innovative drugs through appropriate protection and use of various types of intellectual property generated during the course of drug development, while at the same time respecting intellectual property rights owned by third parties. In some countries, people have difficulty access to healthcare due to economic reasons. To deliver our innovative drugs to more patients worldwide, we will neither apply for nor enforce patent rights in Least Developed Countries defined by the United Nations*1 and Low Income Countries defined by the World Bank*2. We also will not file patent applications or enforce rights in Lower Middle Income Countries defined by the World Bank*3 with the exception of some countries.
In addition, we continue to examine applicability of our patented compounds to Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) and other diseases in the aforementioned countries (use of the existing patent pool, the provision of voluntary licenses to generics manufacturers, etc.).
In the situation of a public health national emergency, such as a pandemic, etc., we understand that the compulsory right will be granted as one of the options. We also understand that the compulsory right will be granted in accordance with Article 31-2 of the TRIPS Agreement (the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) in order to export pharmaceuticals to countries with insufficient or no capacity to manufacture pharmaceuticals. We will consider licensing patents flexibly and appropriately on a case-by-case basis. In order to improve access to pharmaceuticals, granting the compulsory right alone cannot resolve the fundamental problems. We consider that comprehensive activities are necessary, including activities that include the correction of economic discrepancies, training of healthcare professionals, and development of the healthcare system, healthcare infrastructure, and drug supply system.
We aim to create innovative pharmaceuticals and provide a variety of support so that patients can receive the treatment they need. The purpose of the Patient Support Program is to support patients and their families by providing information on treatment and financial support. Our U.S. subsidiary, Deciphera, leverages Deciphera Access Point™ to understand the unique situation of each patient in the U.S. and provides them with a dedicated case manager who helps resolve a wide range of issues covering everything from understanding insurance to financial issues and starting and continuing treatment.
There are still countries and regions in the world where the healthcare infrastructure is immature and many people who cannot access necessary healthcare are left behind. We are working to support NPOs to strengthen the healthcare infrastructure in these regions (local capacity building: Building a healthcare infrastructure where healthcare can be delivered continuously by local capabilities).
Under the "ONO SWITCH Project" that was implemented from FY2018 to FY2021, we have provided support in Cambodia, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Bhutan for the training of local healthcare personnel, educating local citizens on diseases, and assisting with scarce healthcare facilities and supplies (for more details, see "ONO SWITCH Project (FY2018 to FY2022)" on this page below). We have achieved steady results in strengthening healthcare infrastructure through the activities of the NPOs that we supported under this project.
In consideration of the lessons learned from this project, we started a new healthcare access improvement project, the "ONO Bridge Project," in FY2022.
With the new project, and not only through financial support necessary for NPO measures, we will also increase the social recognition of issues related to access to healthcare, have our employees participate in volunteer activities, take measures for collaboration using our know-how, etc. At the same time, we will increase the input of non-financial capital into the project and thereby maximize our social impact and strengthen our human resources, etc. For example, we will increase employee understanding, empathy, and desire to take on the challenge of resolving issues related to healthcare access and we aim to disseminate the mission statement and to increase engagement in the association thereto. In addition, we consider this project as to be an opportunity to broaden our understanding of patients and healthcare issues around the world and thereby aim to support our growth strategy.
![[figure] ONO Bridge Project (Bridging the healthcare access gaps)](https://s3-ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/sustainability-cms-ono2020en-csr-s3/img/social/bridge_project.jpg)
In this project, we works with NPOs to implement the following two programs:Through the programs, we not only contribute to the financial support necessary for NPO measures but we will also increase the social recognition of issues related to healthcare access and take measures for collaboration using our know-how, among other things.


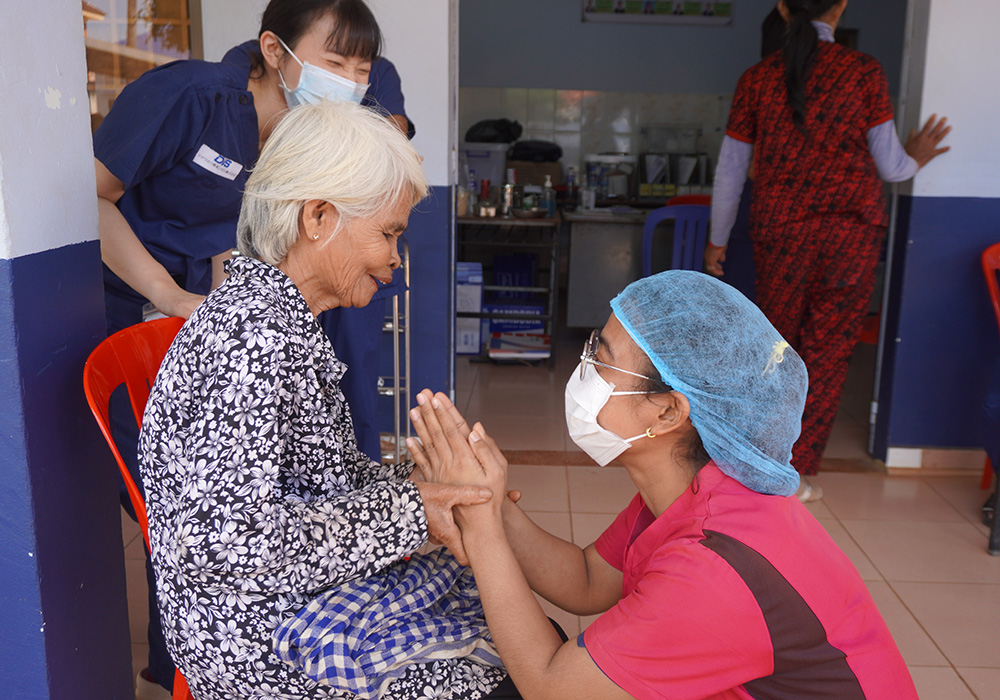
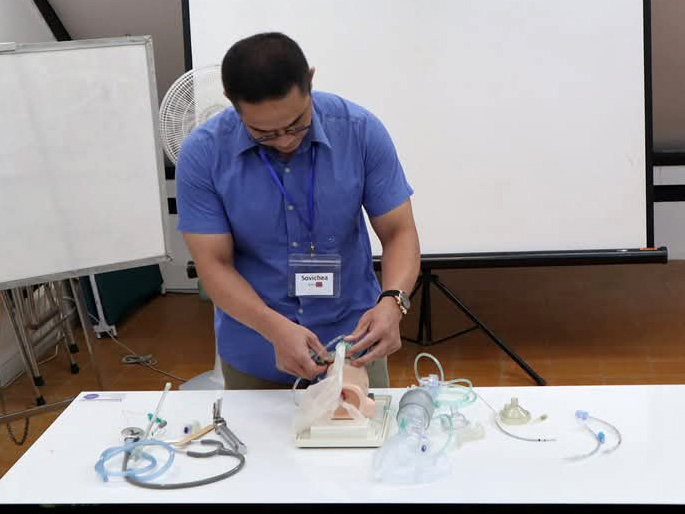
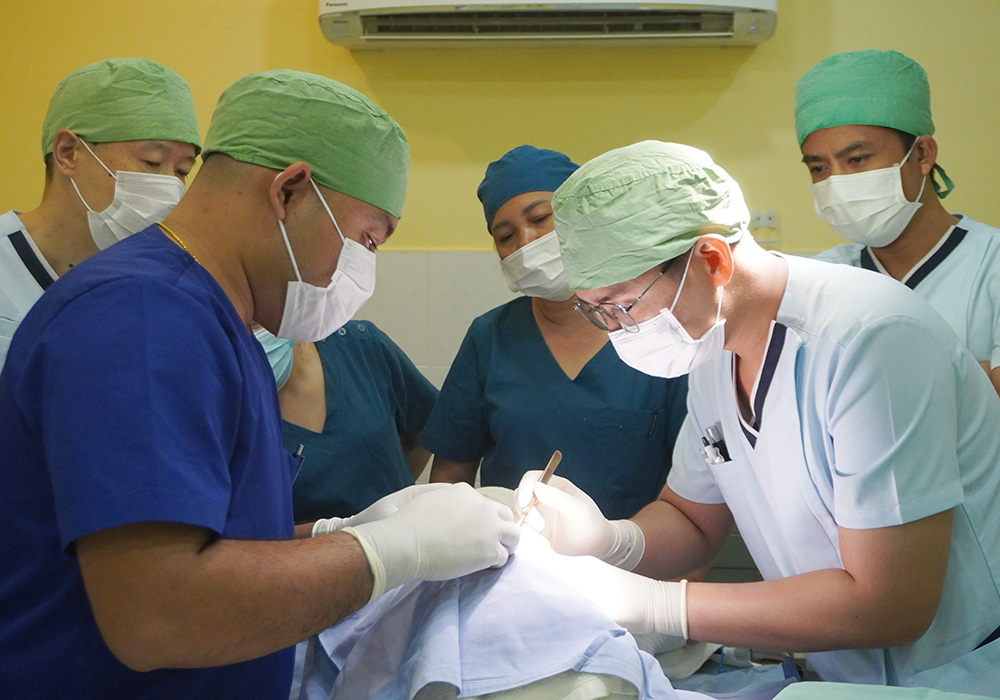
In response to the shortage of medical personnel and knowledge in Cambodia and issues related to accessing medical care in rural areas (economic strength, infrastructure, and local customs), we work with Japan Heart to improve access to medical care for local residents, including pediatric cancer patients, by training medical professionals, educating patients, and providing support to medical facilities through programs.

The United Nations World Health Organization (WHO) has indicated that 80% of patients with pediatric cancer survive in high-income countries, while the percentage of patients who achieve remission in low- and middle-income countries is below 30%*.
Survival rate of pediatric cancer

Many pediatric patients who cannot access advanced medical care have also been left behind in Cambodia.
A major cause is the shortage of medical institutions and healthcare professions that can provide advanced medical care. In particular, due to the impact of history, including the slaughter and civil war that occurred in the past in Cambodia, skilled medical care professionals who train the next-generation of medical care professionals are in short supply and issues related to healthcare access may remain in the future. In addition, the lack of economic power of people in the community, hospital visitation habits, and trust in healthcare are barriers to accessing healthcare.
Japan Heart opened the Japan Heart Children's Medical Center independently in the Ponnel District, Kandal Province, Cambodia, which provides advanced medical care for free to patients with pediatric cancer and other diseases. In addition, Japan Heart also trains local healthcare professionals through its activities. The Medical Center also engages in building the local healthcare system in the Ponnel District and provides free mobile medical services in the district.
Target area: Ponnel District, Kandal Province and surrounding rural areas in Cambodia
From 2022 to 2027
| Initiatives | Target (FY2022-2026) |
FY2022 (~Mar 2023) |
FY2023 (Apr 2023 – Mar 2024) |
FY2024 (Apr 2024 – Mar 2025) |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training skilled healthcare professionals |
|
||||
|
|
― | ― | Completed | |
|
― |
|
|
Completed | |
|
|
|
|
Completed | |
|
|||||
|
― | ― | ― | ― | |
|
|
|
― | on schedule | |
|
|
|
|
― | |
| Inprovement of access to healthcare in rural areas |
|
|
|
― | Completed |
|
― | ― |
|
on schedule | |
| Enhancement of advanced medical devices |
|
|
|
|
Completed |




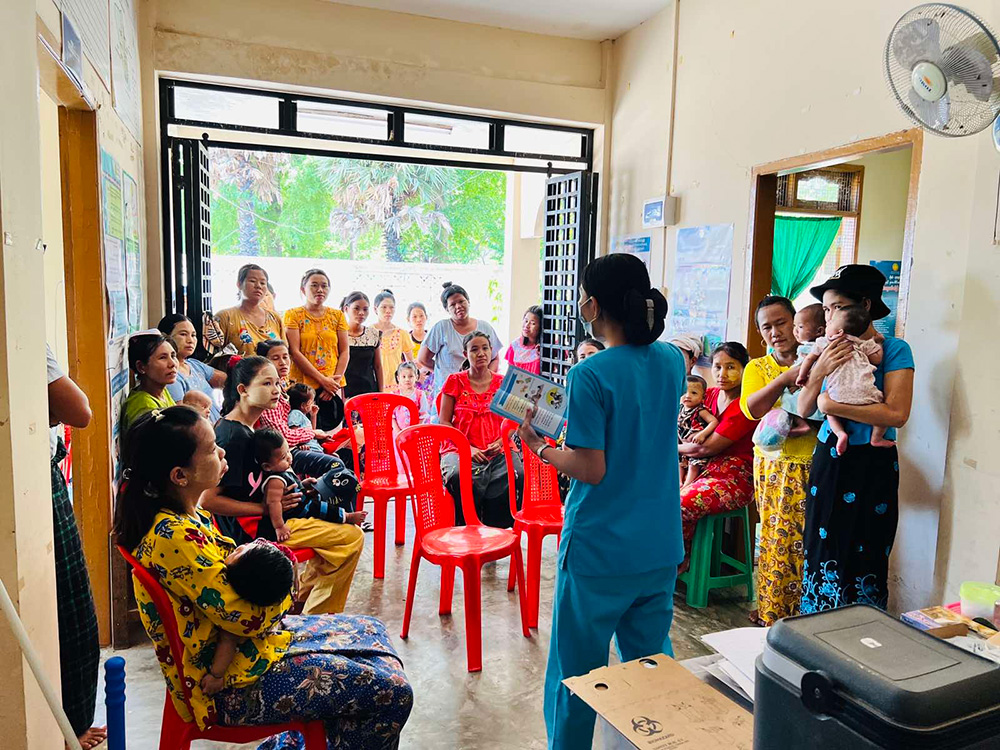
To address the issue of maternal mortality in Myanmar, we will work with PHJ to train maternal and child health care promoters in an aim to help local residents understand the risks of childbirth, strengthen local health service networks that connect local residents and midwives, and to improve access to maternal and child health care services for pregnant and nursing mothers.
The maternal mortality rate in Myanmar is considered to be 250/100,000 live births (source: UNICEF, The State of the World's Children 2021). There is a big gap from the goal: "SDGs 3.1: By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births." One of the causes is childbirth without assistance from healthcare professionals. In addition, the causes include a shortage of healthcare professionals, a shortage of appropriate devices at medical institutions, barriers to physical access, traditions of at-home childbirth, lack of community understanding of the risks associated with childbirth, etc. In addition, this issue is more significant in rural areas and there are differences in access to healthcare even within Myanmar.
Maternal mortality ratio(Per 100,000 live births)

PHJ has engaged with this issue in Tatkone Township, Nay Pyi Taw Union Territory for approximately six years starting in 2014 and achieved results in promoting the use of maternal and child health services in rural areas. PHJ has been expanding the effective models obtained from this activity into Lewe Township Nay Pyi Taw Union Territory since 2020 (we have supported part of this activity).

PHJ aims to increase four indicators (pregnancy check up rate, rate of proportion of births attended by medical practitioners, institutional births rate, and postpartum checkups rate) for which the use rate is particularly low in rural areas.
Percentage of maternal and child health services accessed in the target area (before the start of the program)

Target area: Lewe Township, Nay Pyi Taw
Phase I: January 2023-December 2024
Phase II: January 2025-December 2026
| Initiatives | Target (FY2022-2024) |
FY2022 (Jan - Mar 2023) |
FY2023 (Apr 2023 – Mar 2024) |
FY2024 (Apr – Mar 2024) |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training maternal and child health promoters |
|
|
|
|
Completed |
|
― |
|
|
Completed | |
|
|
|
|
Completed |
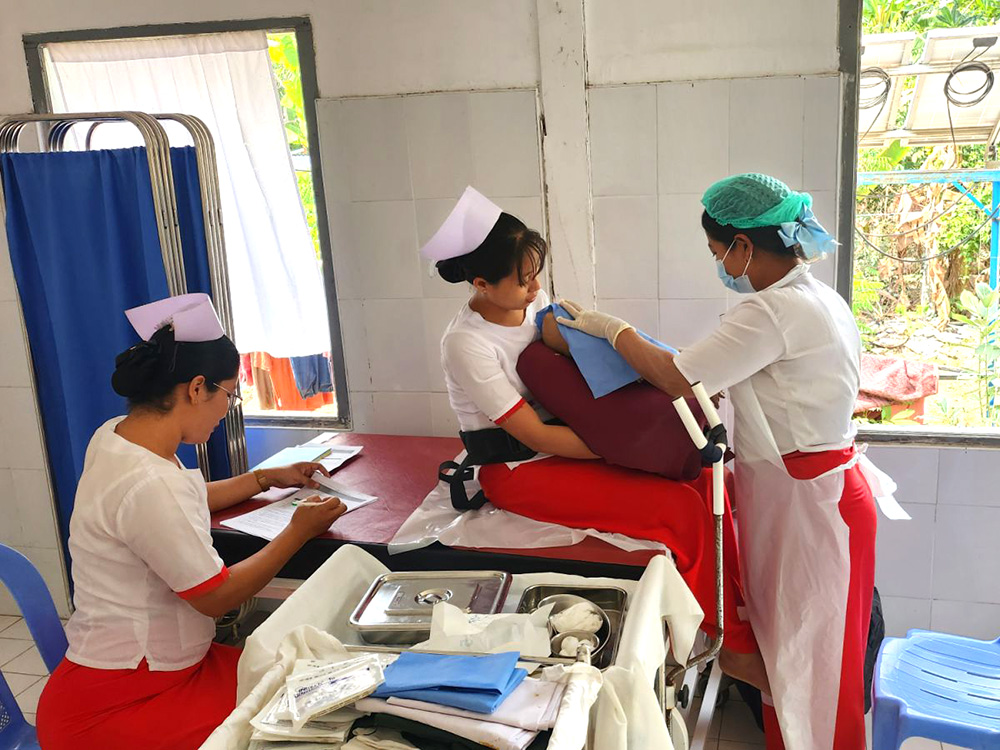
140 maternal and child health promoters were trained in FY2024. Those who completed the training worked together with midwives and auxiliary midwives to visit the homes of pregnant and postpartum women (at least once a month) in the rural areas of the township, encouraged the women to receive health checkups, raised awareness toward infectious disease prevention, and provided support for child vaccinations, among other activities. In addition, a total of 392 health education sessions were conducted.
In addition, for 360 of the maternal and child health promoters we have trained to date, we are re-training them so that they may reacquire knowledge and skills, including reconfirming appropriate health knowledge and learning how to conduct health education sessions and home visits.
Furthermore, amidst an absolute shortage of midwives, skill monitoring (36 midwives) and re-training (38 midwives) were conducted to improve the knowledge and skills of auxiliary midwives (45 in total in the Lewe Township), who play a major role in local maternal and child health care (maternal health checkups, postpartum examinations, childbirth assistance, etc.). This was done to develop health care personnel overall who are responsible for providing maternal and child health care in the region.

| Initiatives | Target (FY2025-2026) |
FY2025 (Jan - Dec 2025) |
FY2026 (Jan - Dec 2026) |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improving access to maternal and newborn health services |
|
― | ― | on schedule |
|
― | ― | on schedule | |
| Strengthening local health systems |
|
― | ― | on schedule |
|
― | ― | on schedule |
We engaged in the ONO SWITCH Project from FY2018 to FY2021 as an initiative to promote both medical system support and work style reform. Under this initiative, donations are made to the medical-related NPOs/NGOs mentioned below who use the money saved by reducing overtime payments through the promotion of our work style reform. The project aims to contribute to the promotion of work style reform, healthcare, and people’s health around the world, thereby further promoting our corporate philosophy “Dedicated to the Fight against Disease and Pain.”
Since 2023, ONO has been participating in Access Accelerated, a global partnership that aims to improve access to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) prevention, treatment, and care in low- and lower-middle income countries.
Access Accelerated is an international initiative which was established at the World Economic Forum in 2017. Its member companies consist of more than 10 pharmaceutical companies in Japan, the United States and Europe. In partnership with organizations such as the World Bank Group, Access Accelerated is working to achieve one of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) targets, namely “By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from NCDs through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being” in low- and lower-middle income countries.
For more information on Access Accelerated activities, please visit the following website.
https://accessaccelerated.org/